Pain and Sport Rehabilitation
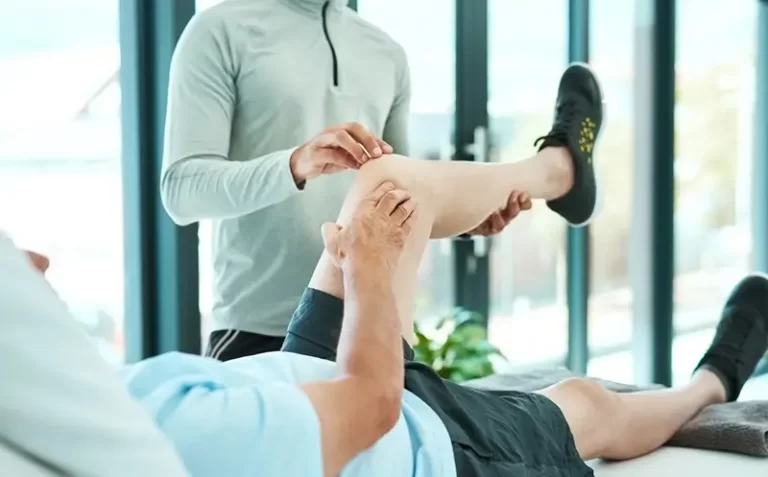

Pain and Sport Rehabilitation
When we talk about pain, it is a symptom that the body exhibits in response to pain stimuli. Pain affects both physical and mental well-being, leading to discomfort and potentially impacting the patient's mood. In more severe cases, it can limit our ability to perform daily activities (functional and activity limitations). There are various definitions of pain, but from a physical therapy perspective, we often categorize it as follows: 1. Acute Pain (0-6 weeks), 2. Sub-Acute Pain (6-12 weeks), and 3. Chronic Pain (more than 12 weeks). The nature of the pain varies depending on the injury location, such as Chronic Low Back Pain or Knee Pain. Apart from the injury location, the type of injury also influences the pain, such as ligament or muscle injuries in the shoulder from exercise (sport injuries) or ankle sprains from accidents.
Due to these factors, it is essential to create a personalized rehabilitation plan for patients experiencing pain. The goal is to select the most appropriate physical therapy methods, both short-term and long-term, to alleviate pain and enable patients to return to their daily activities or sports as normally as possible.
Disease
refers to injuries to various body organs, which can result in pain. Common areas in physical therapy where injuries are frequently observed include muscle injuries, tendon injuries (Tendinitis), and issues with intervertebral discs or joints. Common symptoms that are observed when pain is triggered in the body include:
Acute Pain and Swelling
Pain during muscle contraction (Muscle strain)
Pain when moving or bearing weight on a joint (Pain with Joint Weight Bearing)
Inability to move the joint due to pain (Joint limitation by Pain)
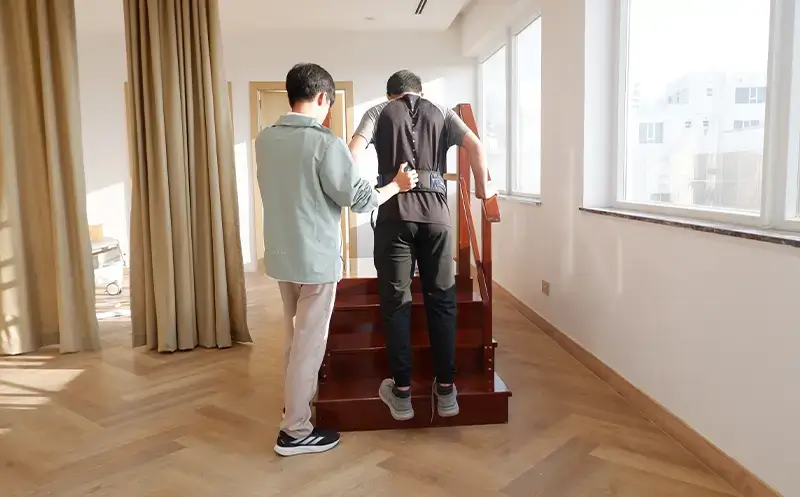
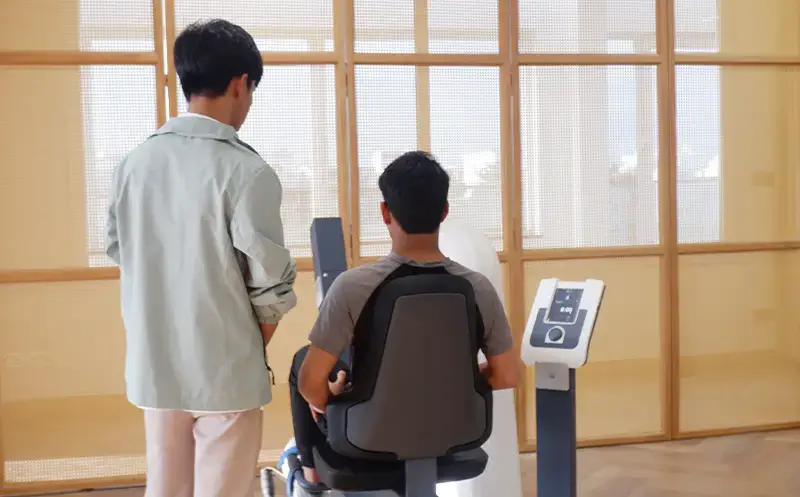


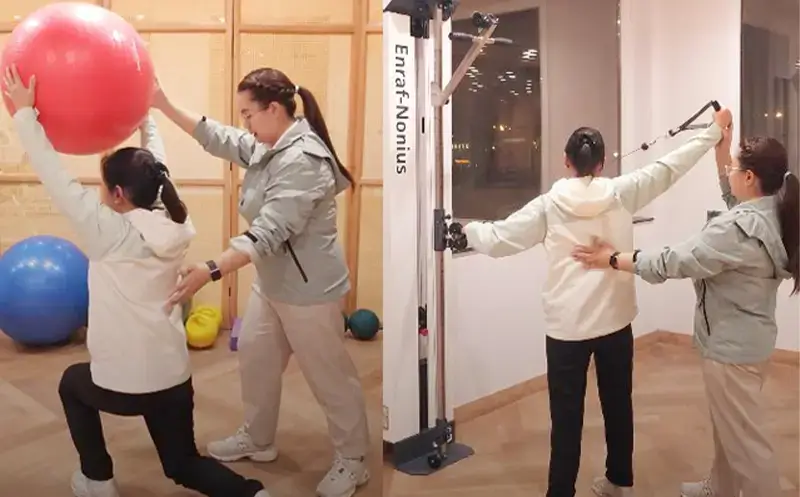
Examples of diseases commonly found include
- Chronic Low Back Pain
- Osteoarthritis of the Knee
- Office Syndrome
- Frozen Shoulder
- Tennis Elbow
- Golfer’s Elbow
- Ankle Sprain
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
- Total Knee Replacement (TKR)
- Herniated Nucleus Pulposus (HNP)
- Lumbar Spondylitis
Physical Therapy for Pain and Sport Rehab
Key Objectives of Physical Therapy
The main goals of physical therapy for this group of patients include assessing pain (Pain Scale) to differentiate pain levels and determine the urgency of pain management.
Evaluating the impact of pain on movement or how it interferes with daily activities to create a treatment plan that is appropriate for each patient.
Selecting the necessary and suitable physical therapy tools for the injury of each patient is a crucial factor. Effective pain management requires collaboration between the physiotherapist, physical therapy equipment, and the patient.
Physical Therapy Assessment
Management of Physical Therapy for Patients with Pain
High Power Laser Therapy
Used to accelerate repair and reduce pain in patients with acute inflammation or post-surgical pain. It can also speed up the healing of infected wounds or pressure ulcers.
Focus and Radial Shock Wave
Uses shock waves to stimulate the repair of chronically inflamed tissues, such as treating chronic heel pain.
Peripheral Magnetic Stimulation (PMS)
Uses electromagnetic waves to inhibit nerve pain, effective in both acute and chronic phases.
Ultrasound Therapy (US)
Increases blood circulation in injured tissues, enhancing tissue repair efficiency and accelerating healing, which helps reduce pain in patients.
Transcranial Electrical Neuromuscular Stimulation (TENS)
Uses low-frequency electrical currents to stimulate the release of opioids, providing pain relief and comfort for patients.
Exercise to Promote and Prevent Pain (Sport Training)
Aims to support pain management and prevention through tailored exercises.
Our Team and Specialists
From the goals and management of the problems in patients with pain mentioned above, there are also important factors that help patients access effective rehabilitation services, which are personnel, especially physical medicine and rehabilitation specialists (Physiotherapist), physiotherapists and occupational therapists, who will help analyze the problem and plan the treatment together.
The Doctor
The doctor will review and predict the severity of the disease and play a part in designing a rehabilitation plan to guide the patient, physiotherapists and occupational therapists.
Physiotherapists in patients with pain
Physiotherapists will focus on assessment and analysis to plan the rehabilitation treatment using specialized tools. With the expertise of the physiotherapist, along with providing advice on preventing pain that may occur, in some patients, physiotherapists can analyze the cause of the injury, such as sports injuries, to lead to planning training or exercises to promote and prevent recurrence.
Occupational therapists in patients with heart and lung systems
Occupational therapists will focus on assessment and analysis to plan treatment for patients, especially in cases where chronic pain affects some functions in daily life, such as wrist therapy in patients with torn wrist tendons, causing the wrist to be unable to function. After pain management, Patients must receive advice and be rehabilitated to return their functions to normal.