Pediatric Rehabilitation
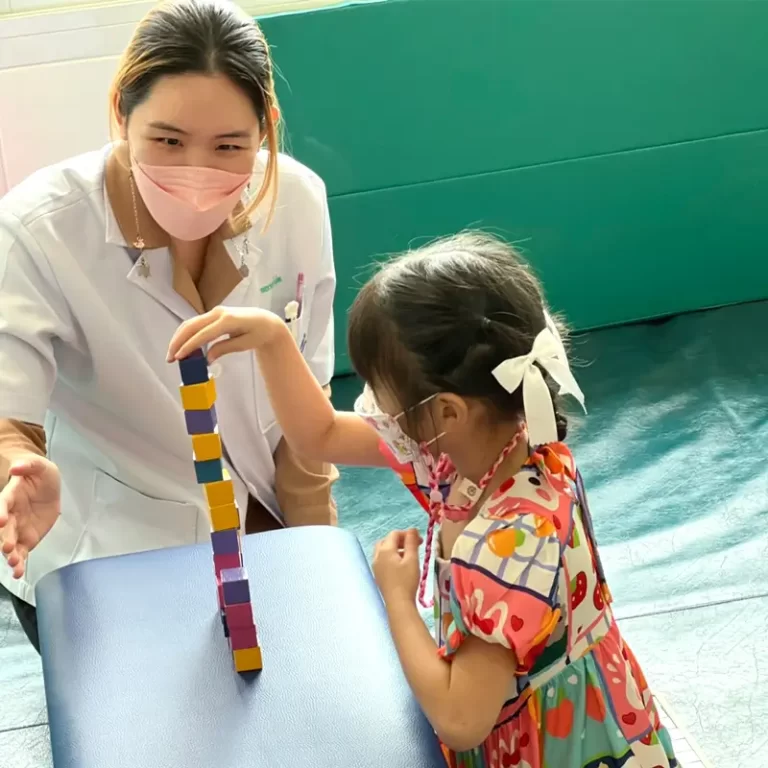

Pediatric Rehabilitation
Whether it is a newborn, an infant, or a child, pediatric patients may suffer from various diseases, which can be broadly categorized into:
1. Pediatric infectious diseases,
2. Neurological disorders, and
3. Cardiopulmonary conditions.
These are common illnesses in children and can significantly impact their growth and development, especially conditions related to the brain. Therefore, physical therapy for pediatric patients is highly necessary and crucial for both the patients and their families. Every child deserves to develop in a manner that is age-appropriate.
Disease refers to disorders that occur in a child's body and organs. Causes may include infections during pregnancy or childbirth, oxygen deficiency during or after birth, genetic abnormalities, or abnormal development of the body or nervous system during pregnancy. When such causes occur, it is essential for every child to receive treatment and developmental assessments to monitor abnormalities at each age stage. Examples of conditions in pediatric physical therapy that require evaluation include:
1. Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)
2. Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)
3. Cerebral palsy
4. Spina bifida
5. Down syndrome
6. Autism
7.Delay development
Physical Therapy for Pediatric Rehab
The primary goal of physical therapy for pediatric patients is to categorize and identify the types of disorders in children through collaboration among physiotherapists, occupational therapists, and parents. This is crucial to accurately assess the severity of the condition and develop an effective rehabilitation plan.
The development of all aspects of a child's growth is vital, and it is essential to provide comprehensive rehabilitation that aligns with the abilities of each individual child.
Physical and occupational therapy should be carried out continuously, both at home and in the hospital.
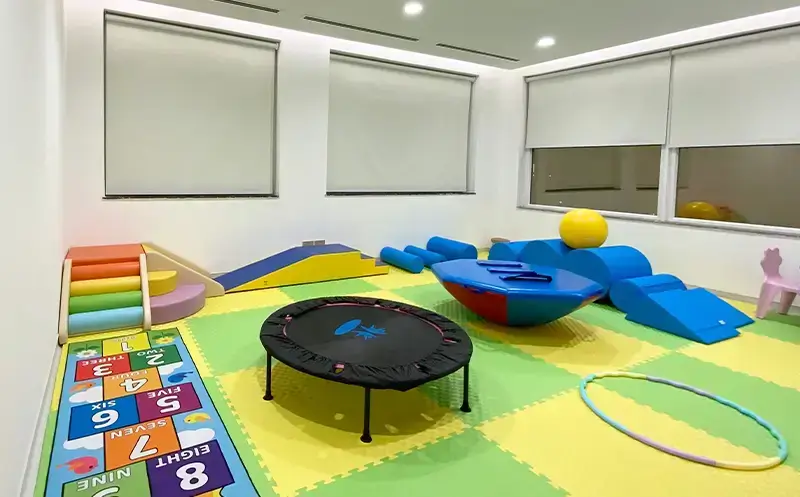
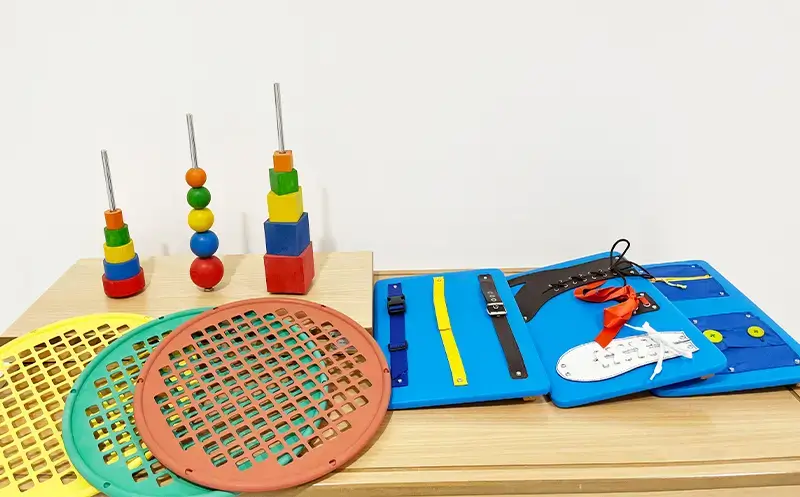
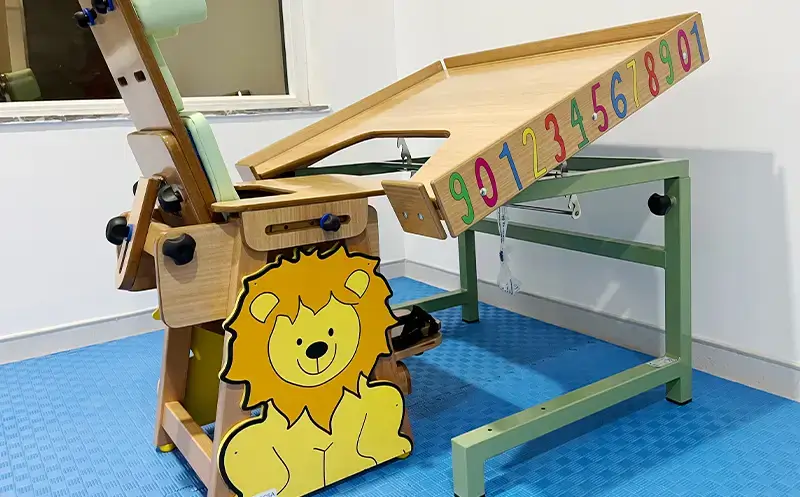



Physical Therapy Assessment
Management of Physical and Occupational Therapy Issues in Pediatric Patients
Management examples often involve two main types of pediatric cases:
Children with Cerebral Palsy
This group often exhibits abnormalities within 3-6 months after birth, when parents notice delayed development or, most noticeably, abnormal body movements
Management and Rehabilitation Methods include:
Physical Therapy
To stimulate the function of large muscle groups (Gross Motor Training) used for body movement, including the torso, arms, and legs. This stimulation is done through play and exercises using pediatric physical therapy equipment.
Occupational Therapy
To stimulate age-appropriate brain development, focusing on fine motor training, such as using the hands for various activities or stimulating cognitive development in areas like analytical thinking and communication. Occupational therapists evaluate and design plans based on the child’s age and developmental stage.
Children with Autism
This is another common condition requiring consultation and assessment by physiotherapists or occupational therapists. The management approach emphasizes analytical thinking, interest in learning, and communication. Children in this group need comprehensive evaluations and personalized occupational therapy plans that incorporate play or individual learning activities. Continuous monitoring and follow-up are necessary until the child reaches school age or becomes more engaged in social interactions.
Our Team and Specialists
From the goals and management of pediatric physical therapy mentioned earlier, a crucial factor that contributes to effective access to rehabilitation services is the personnel, especially specialists in Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Physiotherapists, and Occupational Therapists. These professionals collaborate to analyze issues and plan treatments together.
Doctors review and predict the severity of the condition and play a role in designing rehabilitation plans to guide the patients, physiotherapists, and occupational therapists.
Physiotherapists for Pediatric Patients
Physiotherapists focus on assessing and analyzing to develop rehabilitation plans that enhance motor development. Their goal is to help patients regain the ability to crawl, sit, stand, or walk and reintegrate into society and the external environment.
Occupational Therapists for Neurological Patients
Occupational therapists focus on assessing and analyzing to design treatment plans that improve various developmental aspects, such as analytical thinking, communication, and speech. They aim to stimulate all necessary skills so that patients can achieve near-normal independence.
The multidisciplinary team is essential to ensure that patients and their families can manage issues effectively, especially neurological problems in children that require continuous follow-up and treatment. The ultimate goal is for patients to return to daily life with as much independence as possible.